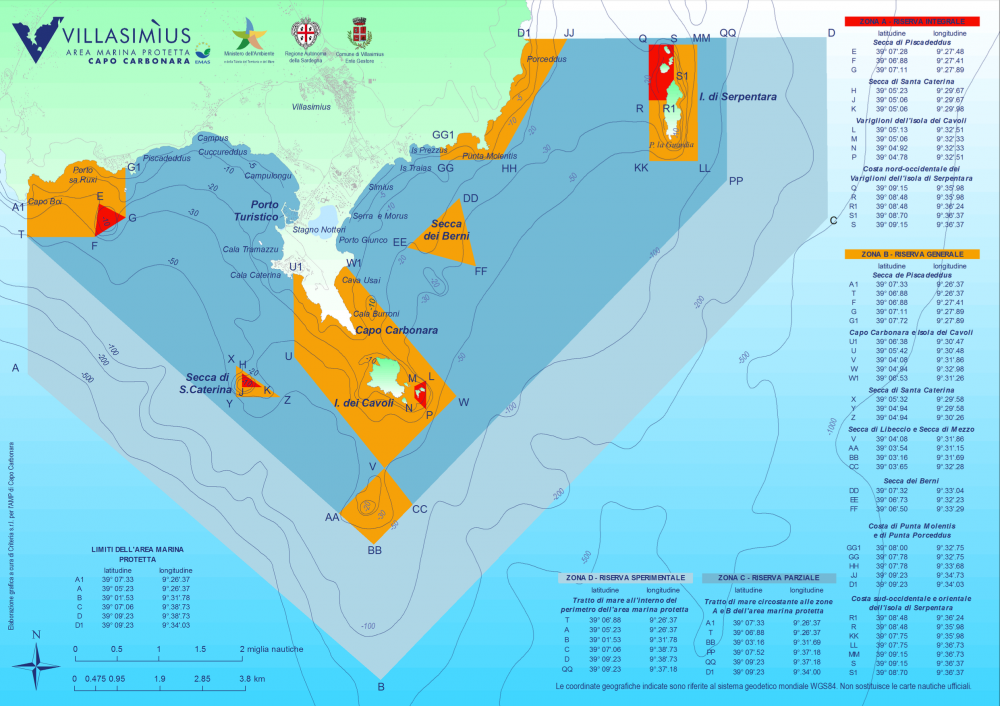
Punta Molentis Beach is part of the Capo Carbonara Marine Protected Area (AMPCC),
established by a Ministry of Environment Decree in 1998, later modified in 1999 and replaced in 2012.
It covers an area of approximately 14,360 hectares, making it the third-largest AMP in Sardinia.
It is divided into four protection levels:
zone A (integral reserve), zone B (general reserve), zone C (partial reserve), and D (experimental reserve).
The managing authority is the Municipality of Villasimius, which, with over 1 million visitors during the summer season,
represents the fourth most important Sardinian area for tourism flows.
The area enjoys significant international recognition,
in 2016 it was awarded as the first sustainable destination in Europe
and in 2018 it was ranked among the top 100 sustainable destinations in the world.
The Capo Carbonara Marine Protected Area was mainly established
to protect its wild and pristine nature, as well as the incredibly diverse marine fauna and flora.
Punta Molentis Beach falls within the second level of protection, which is zone B (general reserve).
In 2012, access was limited during peak season as a measure to safeguard the ecosystem of the area from excessive tourist flow.
Currently, this restrictive measure remains experimental.
All fishing activities are prohibited within the Marine Protected Area.
In zone B, sport fishing may only be carried out if authorized by the managing authority (Municipality of Villasimius).
Zoning Map available below.